As the nuclear charge of the nucleus increases across the period the electrostatic attraction increases between electrons and proton hence the. Ionization energy is the amount of energy necessary to remove an electron from an atom.
What Are The Periodic Trends For Atomic Radii Ionization Energy And Electron Affinity Socratic
Ionization Energy Ck 12 Foundation
Ionization Energy And Electron Affinity
In the 2nd period there is a discrepancy in the trend of ionization enthalpy from boron to beryllium.
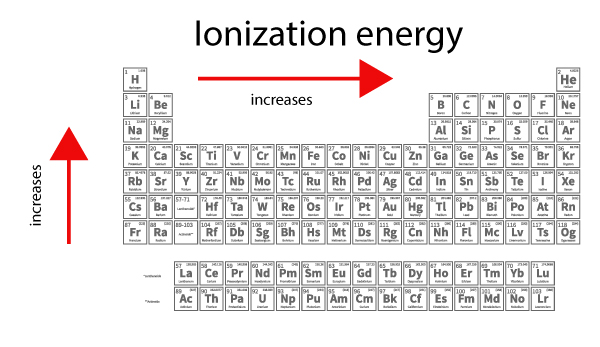
Ionization energy trend. So this is high high ionization energy and thats the general trend across the periodic table. As you go from left to right you go from low ionization energy to high ionization energy. In a group while moving from top to bottom it decreases.
The energy change involved to get 1 mole of gaseous atom from its standard state is known as atomisation energy. The first ionization enthalpy of elements decreases as we move down in a group. Ionization energies of the elements in the third row of the periodic table exhibit the same pattern as those of Li and Be Table PageIndex2.
Atomic radii reported in units of picometers pm. Ionization energy IE is the energy required to remove the highest-energy electron from a neutral atom. The ionization energy tends to increase from left to right across the periodic table because of the increase number of protons in the nucleus of the atom.
Chemical Reactivity decrease as you go left to right of. Ionization energy generally increases across period 3 because the nuclear charge increases but the shielding of the outer electrons remains relatively the same. Another factor is the Electronegativity of the element which determine how badly an element wants to take other electrons from other elements.
Moving left to right within a period or upward within a group the first ionization energy generally increases with exceptions such as aluminium and sulfur in the table above. The first ionisation energy is the energy required to remove one mole of the most loosely held electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms to produce 1 mole of gaseous ions each with a charge of 1. This means that the electrostatic force of attraction between the outer electrons and the nucleus is becoming greater so more energy is needed to remove the electrons.
The atomisation energy for this step is 107 kJmol. It is measured in kJmol which is an energy unit much like calories. Ionization energy Metals Noble gas configuration Noble gases Nonmetals Semimetal Shielding effect 1.
Ionization Energy and Electron Affinity--Similar Trend. Higher energy electrons can have other lower energy electrons between the electron and the nucleus effectively lowering the positive charge experienced by the high energy electron. Main Difference First vs Second Ionization Energy.
Explain why this is so. Xg X g e-It is the. The second ionization energy is that required to remove the next electron and so on.
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. The energy of dissociation of bond energy is 122 kJmol. In general ionization energy increases across a period and decreases down a group.
The energy required to remove the outermost valence electron from a neutral atom is the first ionization energy. The ionization energy of an element increases as one moves across a period in the periodic table because the electrons are held tighter by the higher effective nuclear charge. Across a period effective nuclear charge increases as electron shielding remains constant.
Ionization energy is the amount of energy needed by a gaseous atom in order to remove an electron from its outermost orbitalThis is the ionization energy because the atom gets a positive charge after the removal of an electron and becomes a positively charged ion. Additionally if an electron is being removed from a lower energy level the increased attraction the electron. Data taken from John Emsley The Elements 3rd editionOxford.
Ionization Energy Trends Ionization energies increase for a given atom as successive electrons are removed. The atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus of an atom to the outermost electronsSince the orbitals around an atom are defined in terms of a probability distribution in quantum mechanics and do not have fixed boundaries determining where an atom. The ionization energies associated with some elements are described in the Table 1For any given atom the outermost valence electrons will have lower ionization energies than the inner-shell kernel electrons.
Because positive charge binds electrons more strongly the second ionization energy of an element is always higher than the first. Ionization energy is also a periodic trend within the periodic table. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a specific atom.
Second step involved the dissociation of chlorine molecule to form chlorine atoms in gaseous state. An elements second ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost or least bound electron from a 1 ion of the element. Successive ionization energies increase steadily as electrons are removed from the valence orbitals 3s or 3p in this case followed by an especially large increase in ionization energy when electrons are removed from filled core levels.
This is more easily seen in symbol terms. For example just as ionization energy increases along the periods electron affinity also increases. Positive ions are smaller than the atoms from which they are formed but negative ions are larger than the atoms from which they are formed.
The energy needed to remove the most loosely held electron from a neutral atom. Likewise electron affinity decreases from top to bottom due to the same factor ie shielding effect. Low energy easy to remove electrons.
So if the size of an atom decreases the attractive force between the nucleus and the outermost electrons increases due to which across a period in the periodic table ionization energy generally increases. This is because as each electron is removed the electron-electron repulsion decreasetrons experience greater and greater attraction to the nucleus meaning remaining elec. The first ionization energy of boron is smaller than beryllium and the first ionization energy of oxygen is smaller than nitrogen.
It tends to decrease down a column of the periodic table because the number of electron shells is larger making each ion further away from the nucleus. The attraction of an atom for an additional electron is called electron affinity. Describe the trends in first ionization energy within groups and across periods in the periodic table.
IE increases IE increases. Or especially the first electron and then here you have a high ionization energy. It increases from left to right across a period.
Trend-wise ionization energy tends to increase while one progresses across a period because the greater number of protons higher nuclear charge attracts the orbiting electrons more strongly thereby increasing the energy required to remove one of the electrons. Trends in ionization enthalpy in a group. The shielding effect is the name given to the balance between the attraction between valence electrons and protons and the repulsion between valence and inner electrons.
One factor is Ionization Energy Ionization Energy is how easily and element can remove its electrons. Take for example an alkali metal atom. Both ionization energy and electron affinity have similar trend in the periodic table.
The ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from its orbital around an atom to a point where it is no longer associated with that atom. Ionization energy and ionization potentials are completely different. Ionization Energy Trend in the Periodic Table.
A couple factors will determine how likely and element will react to another element. I know you have trouble seeing that H. The second ionization energy is always higher than the first ionization energy.
Although there is a general trend toward an increase in the first ionization energy as we go from left to right across this row there are two minor inversions in this pattern.

9 Ionization Energy Trends For The Periodic Table Grandinetti Org Download Scientific Diagram

The Parts Of The Periodic Table
Ionization Energy Trends Periodic Table Video Khan Academy

Ionization Energy Wikipedia
Ionization Energy Trend Surfguppy Chemistry Made Easy For Visual Learners

Ionization Energy Trend Science Trends
First Ionisation Energy

Why Is The 2nd Ionization Energy Of Chloride Similar To That Of Sulfur Chemistry Stack Exchange


